
THE ULTIMATE BREAD GUIDE FOR GUT HEALTH
What bread do you eat or do you avoid bread altogether?
There are lots of reasons why we make our food choices, but if you have irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or a food intolerance, your choices can make or break your day.
Did you know there are up to 10 molecules in wheat products that are implicated in IBS and food intolerance symptoms?
Some of these triggers are difficult to isolate, but you can refer to the guide below to better understand the common ingredients that may trigger gut issues in the different types of bread.
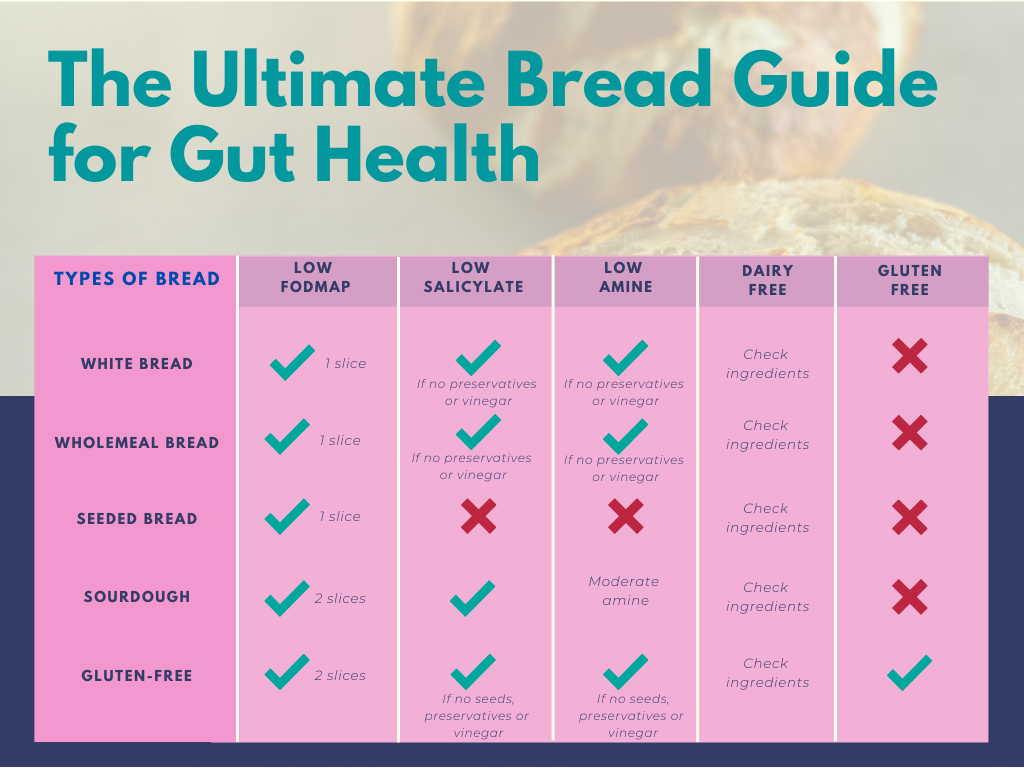
Source: @theguthealthdietitian
What are FODMAPs?
FODMAPs refers to fermentable oligo-, di-, mono-saccharides and polyols and are carbohydrates molecules that are found in wheat, barley, rye and oats along with certain fruits, vegetables, nuts, legumes, sweeteners and some milk products. Do take note that if you are following a low FODMAP diet, some gluten-free ingredients are high FODMAP e.g. onion and garlic. Also, gluten is not a FODMAP and some low FODMAP products contain gluten which will not be an issue.
What are salicylates?
Salicylates are another molecule in food that can also cause IBS symptoms (along with sinus, skin and neurological symptoms) that is different from FODMAPs. Interestingly, salicylates are designed to make living creatures feel sick or unwell. Plants produce them and put them into their fruits, vegetables and leaves. When a bug takes a bite, the salicylate in the plant makes it feel unwell, so it leaves the plant alone. Some people are sensitive to salicylates too.
Salicylates tend to be highest in fresh and underripe fruits and vegetables like capsicum, strawberries, onion, spinach, tomato, herbs & spices, honey and fruit juice.
There is some cross-over woth FODMAPs, so we see changes when a salicylate-sensitive person goes on a low FODMAP diet. A low FODMAP diet can even work well for some time, but then we see unexplained symptoms or it stops working so well.
What are amines?
Amines are similar to salicylates in that they cause IBS-like symptoms along with sinus, skin and neurological symptoms including migraines and anxiety. Amines, however, are related to food ageing and storage, which means that lots of fresh fruits and vegetables are low amine while aged meats and cheeses are higher.
If you have noticed that fresh fruits and salads are well-tolerated (even onion or garlic) but a bolognese sauce or some chocolate causes triggers, even when it’s low FODMAP? If so, it might be amines causing the issues.
Identifying amine sensitivity is a similar process to FODMAPs, as you have to follow an elimination diet followed by food challenges and then finally liberalise to find your individual threshold.
What is gluten?
Gluten is a protein found in wheat, barley, rye and oats. Coeliac disease is a condition where your immune system attacks your own tissues when you eat gluten. This damages your gut (small intestine) which affects your body’s ability to absorb nutrients. Some people do not have coeliac disease, but experience similar symptoms of gas, bloating and abdominal pain due to gluten sensitivity. Researchers are still trying to discover the exact biological cause of this condition, known as non-coeliac gluten sensitivity (NCGS).
Keep this guide handy for your next trip to the bakery or the grocery stores! After all, bread is nutritious and delicious!











